Jatan Mehta • Mar 09, 2022
How we test spacecraft before launch
A space mission is an immensely complex undertaking. Hundreds to thousands of experts from several distinct fields come together to build the thousands of parts and functions of a spacecraft.
To ensure these orchestrate in the harshness of space, where fixing major issues post-launch is either impossible or limited in scope, every spacecraft is extensively tested in facilities that mimic mission conditions.
Launch testing
Anyone who has seen a rocket launch in person (I have!) knows how noisy rockets are, the rumbles of which can be heard across great distances. A spacecraft sitting on top of a rocket needs to avoid mechanical damage from this intense, sustained acoustic noise.
To ensure this, spacecraft are tested before launch in special acoustic chambers, like the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Large European Acoustic Facility. The chamber has large stereo-speaker-like noise horns that simulate launch sounds while noise absorption coatings sustain the noise and cause reverberations.
A spacecraft’s structure also needs to survive the jolt from rocket engines turning on and the vibrations they generate during flight. For this, all spacecraft — and sometimes even their individual components — are tested pre-launch on electric or hydraulic shaker tables, which simulate a rocket’s intense vibrations. ESA’s HYDRA facility can generate vibrations equivalent to an earthquake of 7.5 on the Richter scale.
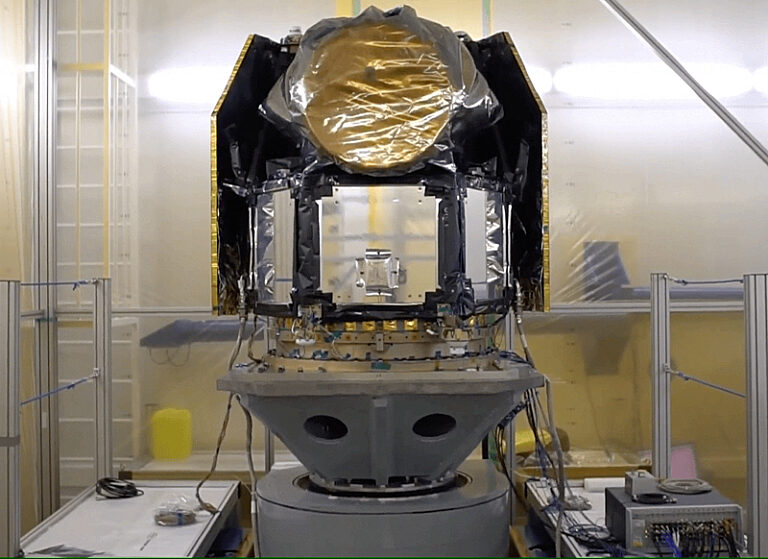

Simulating space
A spacecraft orbiting a world can experience environmental temperature swings from blazing heat when sunlit to frigid cold at night in a matter of hours. The sudden, repeated heat variations can cause materials of the spacecraft to unevenly expand and contract, potentially leading to fractures over time. Moving parts may also fail. For this purpose, every spacecraft’s range of functionality is tested for weeks or even months in thermovac chambers — also called space simulators — which achieve a space-like vacuum and simulate extreme temperature swings. Powerful xenon lamps and mirrors simulate space’s unfiltered sunlight, with varying intensities based on if the mission will take a spacecraft closer to the Sun, like NASA’s Parker Probe, or away from the Sun, like Juno. Spacecraft that will explore a planetary surface such as Mars go through additional tests with temperatures and atmospheric pressures similar to that on the planet.
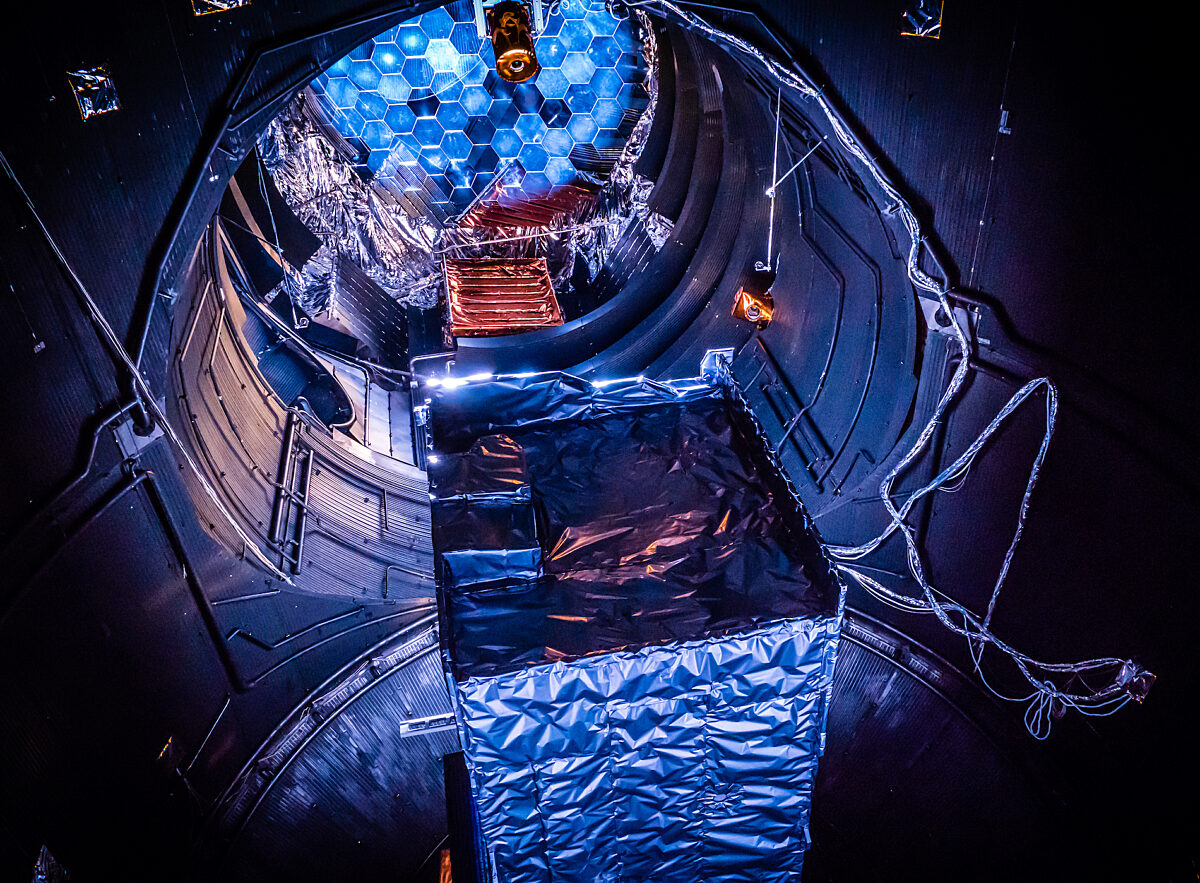

NASA’s Space Power Facility at the Glenn Research Center's Space Environments Complex is the world’s largest vacuum chamber, and has been used to test not just spacecraft but also rocket fairing separations, Mars landing systems, solar array deployments, and much more.
More core tests
Since terrestrial electronics don’t (reliably) work in harsh space environments, spacecraft computers are built using hardened components tested in more than 100 ways to reduce radiation and mechanical damage.
Each spacecraft’s software is also tested rigorously, because while it can be patched post-launch, the extent is limited. Testing often happens in stages. For example, NASA tested the Perseverance rover’s navigation and landing software over seven years, starting with it running on Mars rover computer models, followed by mission-relevant sensors, and lastly on actual Mars-bound hardware.
There are also tests to prevent a spacecraft’s own instrument noises from ruining the mission. Faraday Cage chambers, which have foamy interiors to block outside electromagnetic radiation, are used to understand a spacecraft’s own electrical and radio noises, and ensure they don't interfere with each other and affect scientific observations or damage onboard electronics.
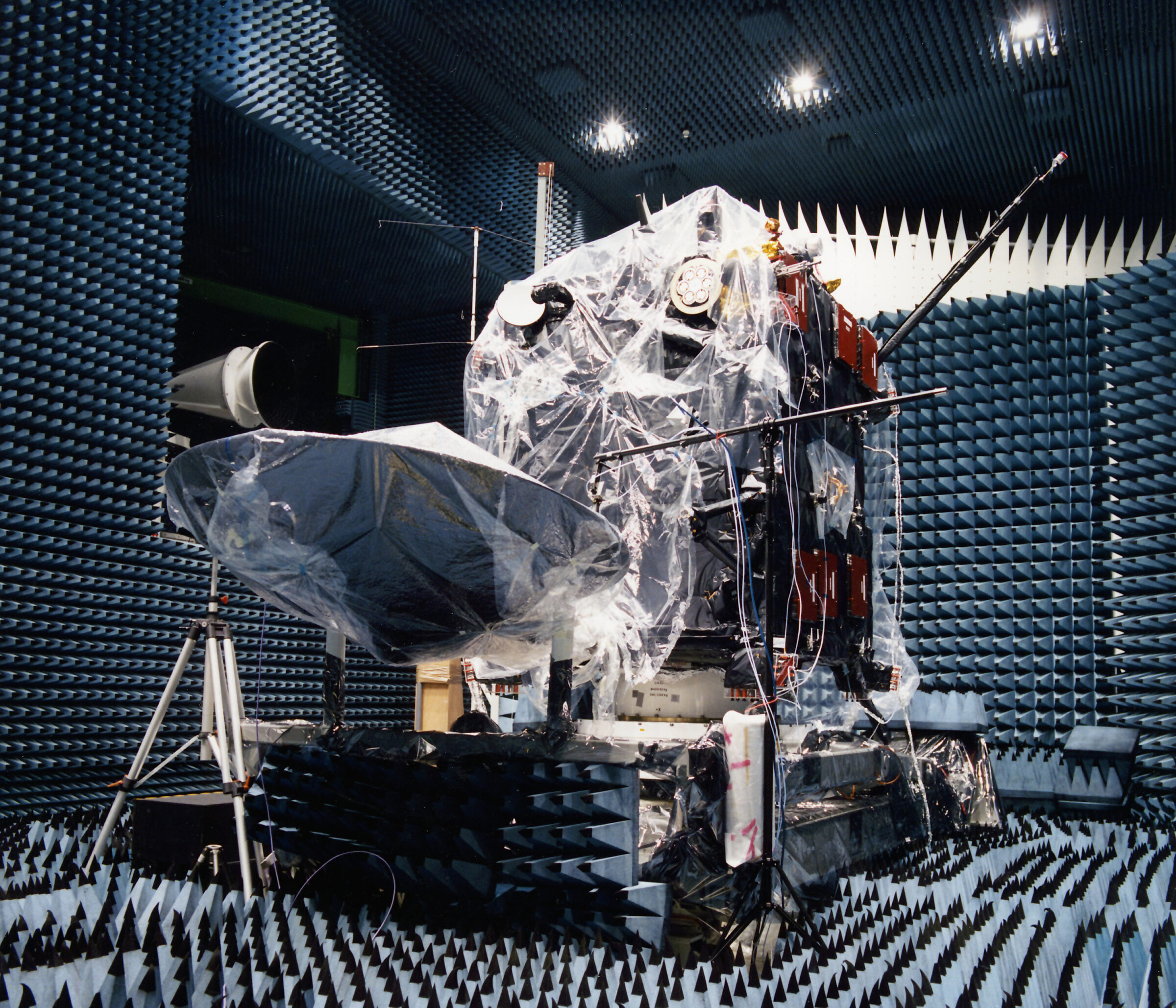
Likewise, spacecraft that will study magnetic fields — such as those of Earth, the Sun or Jupiter — are placed in special chambers to ensure magnetic noises from their instruments are contained. ESA’s IABG has one such remote test facility, which avoids interference from civilization-generated magnetic fields thanks to its location in a forest and the fact that it's made of non-magnetic materials such as wood. It also has large 15-meter (49-foot) coils to offset Earth's magnetic field to ease spacecraft testing.
Additional tests for each spacecraft can vary as greatly as the missions themselves. These include specialized antenna testing for communications, optical testing for cameras and telescopes, helicopter-based radar testing for missions studying subsurfaces of planets and moons, deployment mechanism tests for space telescopes like JWST, heat shield and parachute testing for Mars landing missions and crew capsules returning to Earth, and more.
Meeting mission-specific needs
Many times entirely new facilities have been created for cutting-edge missions. For example, ESA created the Wide Range Test Facility to test their upcoming JUICE spacecraft’s ability to survive temperatures as low as -230 degrees Celsius (-382 degrees Fahrenheit), which is what it can experience when Jupiter or its moons eclipse the Sun.
The Indian space agency ISRO developed a lunar soil simulant and terrain to test their Chandrayaan landers and rovers. For the VIPER rover mission, which will traverse through some of the most challenging terrain in the solar system, NASA tested roving a model of its wheel in simulated lunar terrain for more than 40 kilometers of varying slopes and rock distributions.

As NASA prepares to send humans to the Moon again, it’s been thoroughly testing the design of its crewed Orion spacecraft that will splash down in the Pacific Ocean at the end of each mission. This includes practicing recovering mock Orion capsules in sea, wind tunnel testing of heat shield components, water drop tests and more.

The road to space
Spacecraft tests aren’t necessarily conducted with the final mission hardware since damage to some delicate parts or intricate functions could cost a lot of money and delay the mission. This risk is often worked around by building representative models of spacecraft or their parts for testing.
But even in a scenario where things proceed smoothly to the launchpad, spacecraft testing is a time-consuming process. This is why space agencies often have several test facilities in one place, such as ESA’s European Space Research and Technology Center, India’s ISRO Spacecraft Integration Test Establishment, and NASA’s Space Environments Complex.
To learn more about how spacecraft are tested, you can check out the virtual tours of test facilities by ESA and NASA.
Support our core enterprises
Your support powers our mission to explore worlds, find life, and defend Earth. You make all the difference when you make a gift. Give today!
Donate

 Explore Worlds
Explore Worlds Find Life
Find Life Defend Earth
Defend Earth

