Ted Stryk • Mar 05, 2015
Venus From 33 Years Ago, and Why We Need to Explore
This article originally appeared on Ted Stryk's blog and is reposted here with permission.
Thirty-three years ago today, Venera 14 plunged down through the thick Venusian atmosphere to the surface, where it successfully operated for 57 minutes. Like the three imaging landers before it, its cameras scanned back and forth across the surface while other instruments took measurements. The cameras would touch the horizon at either end of the panorama and dip down to the foot of the lander in the middle, a compromise which allowed images to be returned showing both the foreground and the horizon while having adequate resolution to be interpretable and to still be returnable during the short surface mission. Venera 14, as it happened, landed at a very rocky site. Being tipped a bit, one of its cameras barely touched the horizon, while one side of the other camera gave the most sweeping view of the Venusian horizon we have.

On the opposite side, the landing managed to dislodge a piece of the rocky surface.
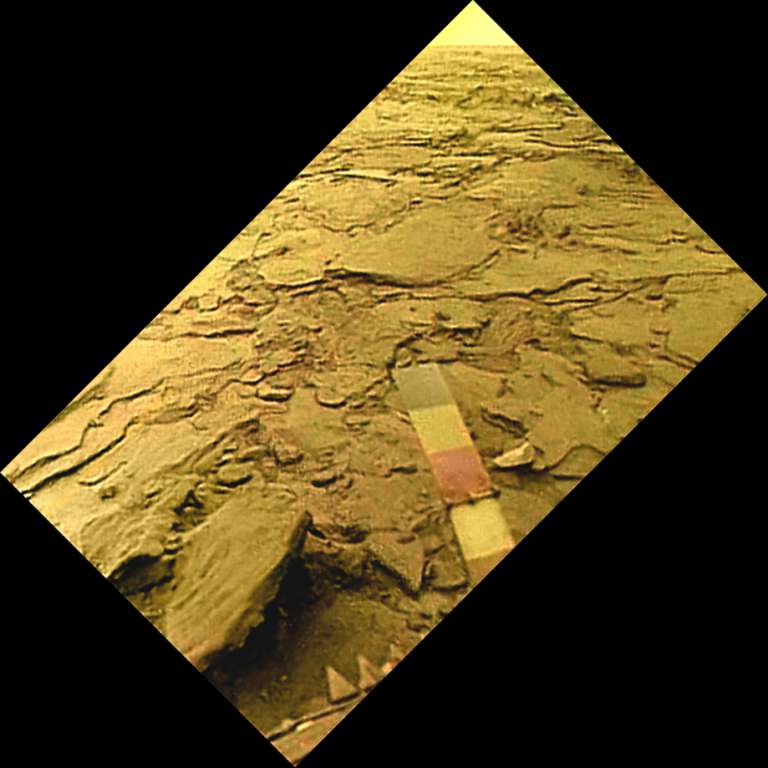

Venera 14 showed a rocky, harsh surface with little regolith/soil compared to the other landing sites. This brought to mind a talk I heard last fall, in which Victor Baker criticized the vain attempts to find a single site to send a rover where it could tell the whole story of Mars. As Baker said, imagine finding a site where the story of Earth could be told by roving a few kilometers! The three Martian sites we've sent stationary landers and four sites we've sent rovers are grossly inadequate. That despite the fact that we have sub 10-meter coverage of nearly the whole planet and resolution of a few tens of centimeters over great swaths of the planet.
Venus is much larger than Mars - nearly the size of Earth! Yet we have only landed in four places and done very limited imaging and surface science at those sites. We have, granted, landed at four more sites where imagery was not taken, but less than half a day, collectively, has been spent operating on the surface, while the shortest-lived Mars landers had lifespans measured in months, most lasted years, and one has lasted more than a decade. And many of them roved the surface, covering multiple terrain types. Beyond the four Venera sites that were imaged, the next best images we have are radar images taken at a scale of 70-100 meters per pixel, the size of a football field! And despite the fact that all four landers landed in roughly the same area of the planet, the terrain at each site was markedly different. The above images were balanced to better bring out detail, these balanced (or in some cases colorized) to be more along the lines of how I think the surface might actually look.
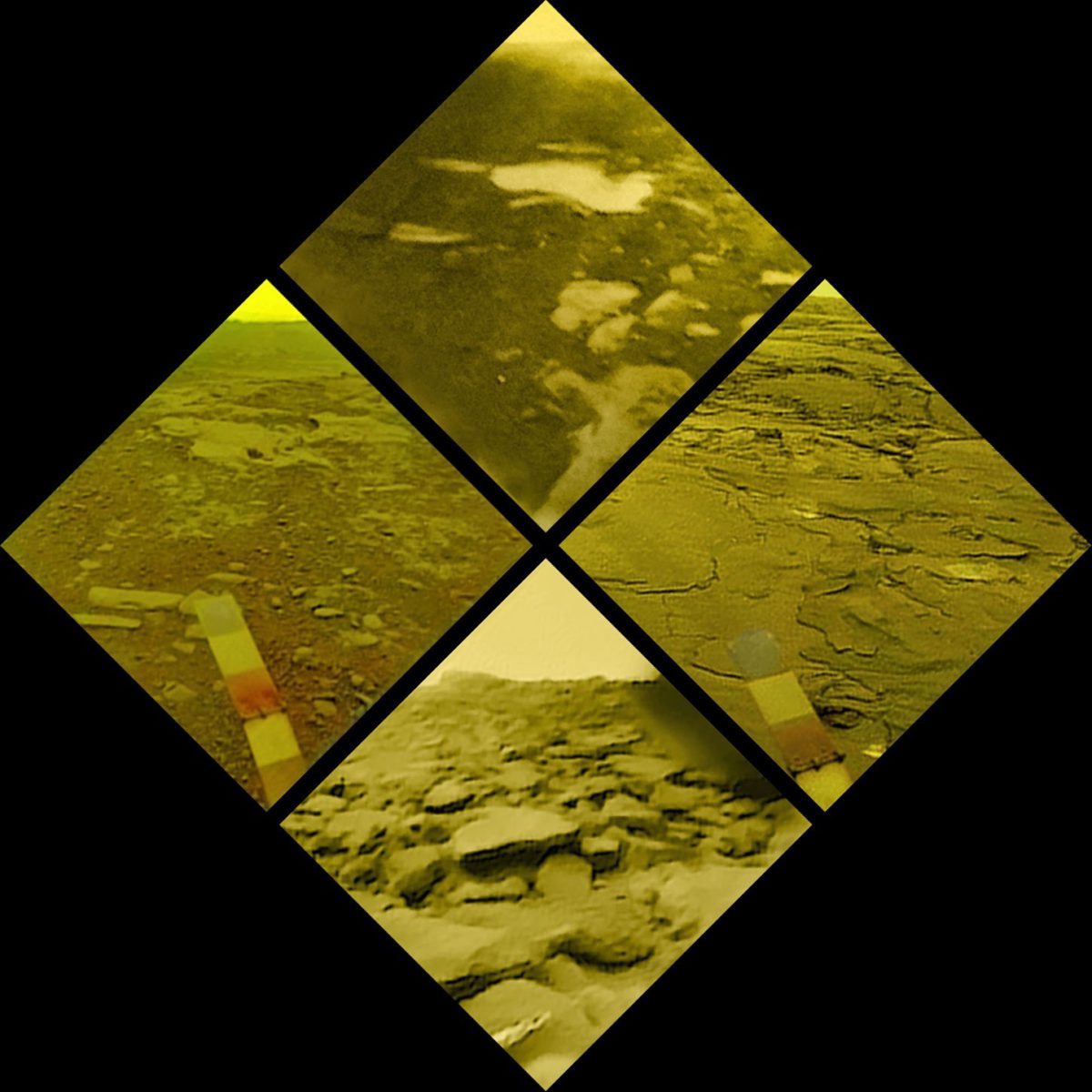
Here is the same set, tipped upright:

This is the tip of the iceberg when to comes to terrain types, and even these landscapes were barely touched. Below is the widest panorama that can be made by combining the panoramas, and even it is patchy and of poor resolution.

Sadly, other than orbiters that primarily studied the atmosphere, Venus has been left alone since the end of the Magellan radar mapping mission in the early 90s. The final lander accomplished its mission, albeit with no camera, on June 15, 1985. We need to go back!
Around 6:00 UTC on March 5, 1982, this picture was being returned by Venera 14 as it fell silent forever. It remains humanity's last view from the surface of Venus.

EDIT: Here is a second interpretation of the color for the combined set, with an attempt to improve the balance. I can't decide which one I think is more accurate.

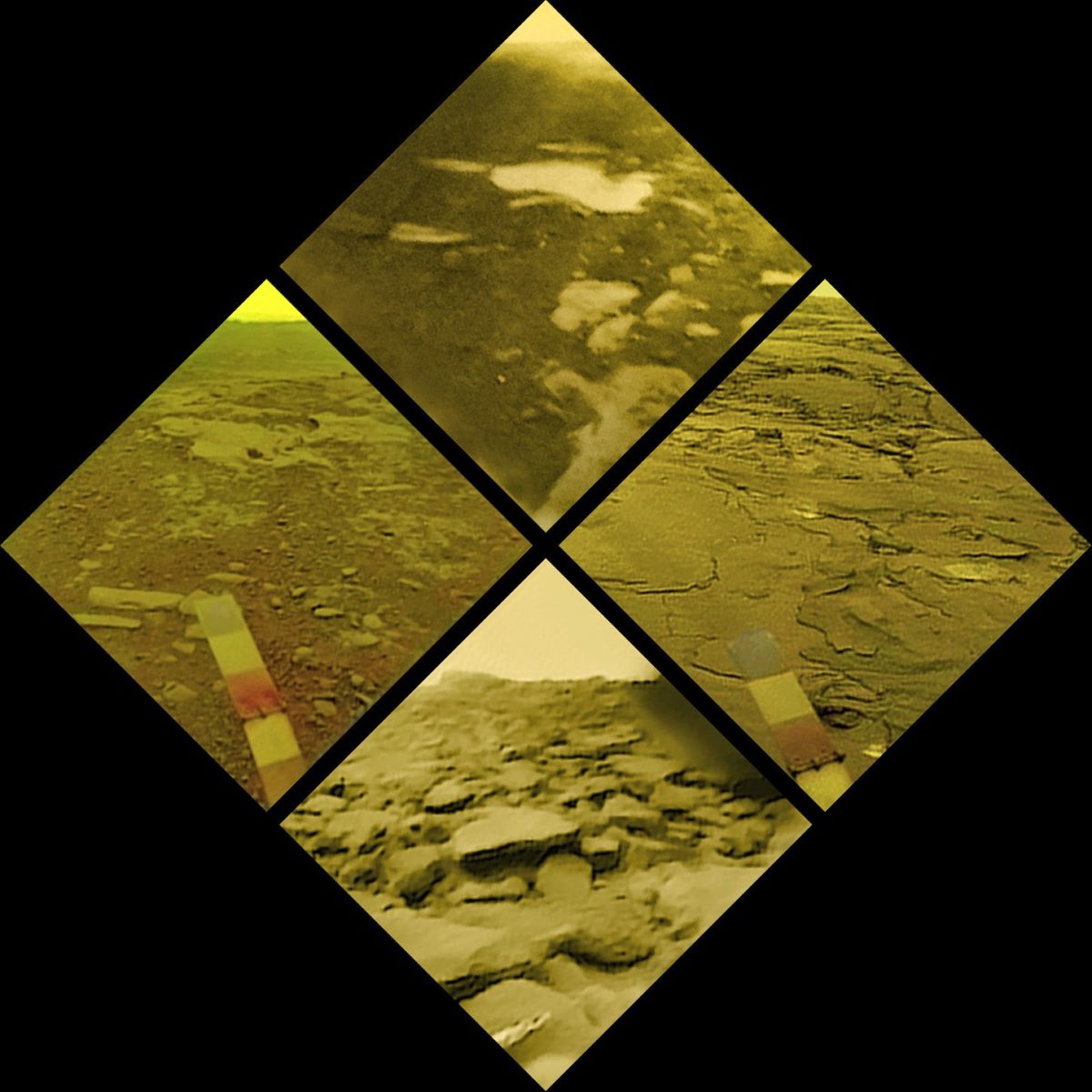
Data courtesy the Russian Academy of Sciences, processed images copyright Ted Stryk.


 Explore Worlds
Explore Worlds Find Life
Find Life Defend Earth
Defend Earth

